Echolink
Related Wiki pages: IRLP, D-Star
Introduction
Echolink is a VOIP (Voice Over IP) application that allows amateurs to connect to one another using the internet. It is similar to IRLP, but allows users to connect via either radio or computer. Application versions are available for PC and Mac computers. Echolink is not usually described as a digital mode - although VOIP is digital transmission of voice - as most operators will use an FM radio to connect to the echolink network.
VOIP connections of any sort - including Echolink - require a DSL connection to the internet. A minimum connection speed of 256KBs is usually recommended for effective, clear VOIP applications.
Using Echolink on a computer
As Echolink is an uses internet protocols for transmission of voice, various ports must be open in your firewall for it to operate properly, the Echolink website summarising the requirements thus:
- Allow UDP destination ports 5198-5199 between Internet and PC in both directions
- Allow TCP (source port any, destination port 5200) from PC to Internet
Because the firewalls only allow port directs to particular IP addresses - and hence computers - Echolink can in most cases only be used on one computer at a time in a particular household. Some ISP's may allow multiple unique external IP addresses, in which case echolink can be used on multiple computers.
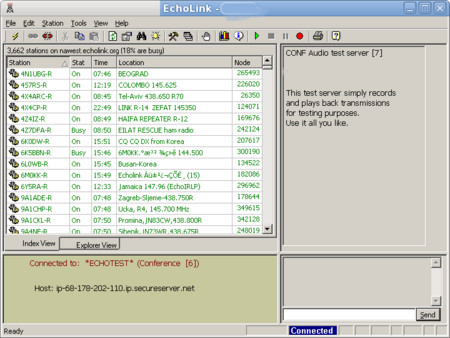
The Echolink application presents a window such as the one below to the user.
The user selects a contact from the list and communication is carried out using the computer microphone.
Using Echolink via a radio
Step by step process
- Look here to find out which nodes are available and where they are located. This list is updated regularly, and gives information about which nodes are connected to each other. If you use Google Earth, this kmz file will show you the connections between Echolink nodes.
- Locate a node close to you and one that you would like to contact. Repeater listings such as this one for Australia, will provide useful information in your search.
- Use a DTMF microphone and dial in the node number that you wish to contact. A message will tell you if you either are successful or unsuccessful.
- There will be a delay between sending and receiving when using Echolink or IRLP. Best protocol is to wait a couple of seconds between hearing the other person and starting to talk yourself.
- When you have finished talking, use the DTMF buttons and dial in 73. This will disconnect the nodes.
[[|EchoLink DTMF Functions]]
EchoLink can be configured to accept commands through the local radio receiver using DTMF tones (TouchTones). These commands are used to enable or disable the link, or to connect or disconnect a station on the Internet.
Each command consists of a sequence of digits (or the special keys *, #, and A through D). Although a set of default sequences is assigned to each function, any sequence can be customized using the DTMF tab of the Sysop Settings page.
The table below lists each of the DTMF commands.
//Note:// If you have upgraded from an earlier version of EchoLink, you may need to choose “Reset to Defaults” to make all of the following commands available.
Command |
Description |
Default |
Connect |
Connects to a station on the Internet, based on its node number. |
num |
Connect by Call |
Connects to a station on the Internet, based on its callsign. |
C+call+ |
Random Node |
Selects an available node (of any type) at random, and tries to connect to it. |
00 |
Random Link |
Selects an available link or repeater (-L or -R) at random, and tries to connect to it. |
01 |
Random Conf |
Selects a conference server at random, and tries to connect to it. |
02 |
Random User |
Selects an available single-user station at random, and tries to connect to it. |
03 |
RandomFavNode |
Selects an available node (of any type) at random from the Favorites List, and tries to connect to it. |
001 |
RandomFavLink |
Selects an available link or repeater (-L or -R) at random from the Favorites List, and tries to connect to it. |
011 |
RandomFavConf |
Selects a conference server at random from the Favorites List, and tries to connect to it. |
021 |
RandomFavUser |
Selects an available single-user station at random, and tries to connect to it. |
031 |
Disconnect |
Disconnects the station that is currently connected. If more than one station is connected, disconnects only the most-recently-connected station. |
|
Disconnect All |
Disconnects all stations. |
## |
Reconnect |
Re-connects to the station that most recently disconnected. |
09 |
Status |
Announces the callsign of each station currently connected. |
08 |
Link Down |
Disables EchoLink (no connections can be established). |
(none) |
Link Up |
Enables EchoLink. |
(none) |
Play Info |
Plays a brief ID message. |
* |
Query by Call |
Looks up a station by its callsign, and reads back its node number and status. |
07+call+ |
Query by Node |
Looks up a station by its node number, and reads back its callsign and status. |
06+num |
Profile Select |
Switches to a different stored set of configuration settings (0 through 9). |
B#+num |
Listen-Only On |
Inhibits transmission from RF to the Internet. |
0511 |
Listen-Only Off |
Restores normal transmission from RF to the Internet. |
0510 |
Connect
The default for the Connect command is to simply enter the 4- 5-, or 6-digit node number to which you wish to connect. To prevent interference with other DTMF functions, however, you may wish to configure a special prefix, such as A or 99.
Link Up and Link Down
No defaults are provided for these functions. To enable these functions, enter a DTMF sequence for each one, using the DTMF tab of the Sysop Settings page.
Profile Select
Profiles are numbered from 0 to one less than the number of profiles shown under File→Profiles. Profile 0 is always MAIN.
Station Shortcuts
Custom DTMF commands can be created to connect to specific stations. These commands are called Station Shortcuts, and are not shown in the table above. To manage your Station Shortcuts, click the Station Shortcuts button on the DTMF tab of Sysop Settings.
Entering Node Numbers
To enter a node number (for the Connect or Query by Node commands), enter the 4-, 5-, or 6-digit node number. If the specified node is not among the stations currently logged on, EchoLink will say “NOT FOUND”.
Entering Callsigns
To enter a callsign (for the Connect by Call or Query by Call commands), press two digits for each letter and number in the callsign. The first digit is the key on which the letter appears (using 1 for Q and Z), and the second digit is 1, 2, or 3, to indicate which letter is being entered. To enter a digit, press the digit followed by 0. When finished, end with the pound key (#).
For example, the letter “K” is entered as “52”, the letter “Q” is entered as “11”, and the digit “7” is entered as “70”.
| 1 Q-11 Z-12 |
2 A-21 B-22 C-23 |
3 D-31 E-32 F-33 |
A |
4 G-41 H-42 I-43 |
5 J-51 K-52 L-53 |
6 M-61 N-62 O-63 |
B |
| 7 P-71 R-72 S-73 |
8 T-81 U-82 V-83 |
9 W-91 X-92 Y-93 |
C |
| * | 0 | # | D |
Callsigns need not be entered in full. If a partial callsign is entered, EchoLink will find the first match among the stations currently logged on. If no match is found among the stations currently logged on, EchoLink will say “NOT FOUND”.
Examples
(These examples assume that the default DTMF codes are configured.)
* To connect to node number 9999: * Enter: 9 9 9 9
EchoLink responds with:
“CONNECTING TO CONFERENCE E-C-H-O-T-E-S-T”
followed by
“CONNECTED”
because 9999 is the node number of conference server ”*ECHOTEST*”.
* To get the status of K1RFD:
Enter: 0 7 5 2 1 0 7 2 3 3 3 1 #
EchoLink responds with:
“K-1-R-F-D 1-3-6-4-4 BUSY”
because 13644 is the node number of station K1RFD, and K1RFD is currently busy.
* To connect to a random link or repeater:
Enter: 0 1
EchoLink responds with:
“CONNECTING TO K-1-O-F REPEATER”
followed by
“CONNECTED”
because K1OF-R was selected at random.
Getting Help
The Echolink community provides a number of forums for users to get assistance:
- Echolink support page
- Echolink Help files These are available in PDF.
- Yahoo group for echolink users
| Modes of operation | |
| Modes | CW * AM * FM * SSB * Digital * Echolink * Emission Classification * IRLP * Optical communications |
| Packet | APRS * D-Star |
| SSTV and ATV | SSTV frequencies * SSTV Modes |