Dish or Parabola: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Protected "Dish or Parabola" [edit=autoconfirmed:move=autoconfirmed]) |
(added diagrams) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Parabolic Geometry == | == Parabolic Geometry == | ||
[[Image:Vk4yeh_parabolic_geometry.jpg | 600px]] | |||
A Parabola is one of the “conic sections” and is defined as the locus (path) of a point that travels so that it is equidistant from a fixed point and a straight line. Algebraically this can be reduced to: | A Parabola is one of the “conic sections” and is defined as the locus (path) of a point that travels so that it is equidistant from a fixed point and a straight line. Algebraically this can be reduced to: | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Finding the focal length of a parabolic dish == | == Finding the focal length of a parabolic dish == | ||
[[Image:Vk4yeh_focal_point.jpg |600px]] | |||
<math> f = \frac {D^2}{16d} </math> where '''D''' is the diameter of the dish and '''d''' is the depth of the dish | <math> f = \frac {D^2}{16d} </math> where '''D''' is the diameter of the dish and '''d''' is the depth of the dish | ||
Revision as of 02:23, 5 August 2008
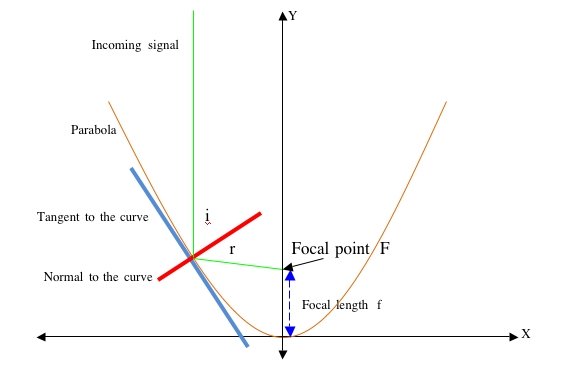
Parabolic Geometry
A Parabola is one of the “conic sections” and is defined as the locus (path) of a point that travels so that it is equidistant from a fixed point and a straight line. Algebraically this can be reduced to:
<math> y = ax^2</math> where a is a constant
More specifically, <math> y = \frac{x^2}{4f} </math> where f is the focal length – distance from the curve to the focal point
In the diagram above:
- the Y axis is central to the curve
- the tangent is a line that touches the curve at one point and has the same gradient as the curve at that point
- the normal is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact with the curve
- i is the angle of incidence – the angle between the incoming signal and the normal
- r is the angle of reflection – the angle between the reflected signal and the normal
- i = r Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
- a broad beam entering the parabola will be reflected to and concentrated at the focal point
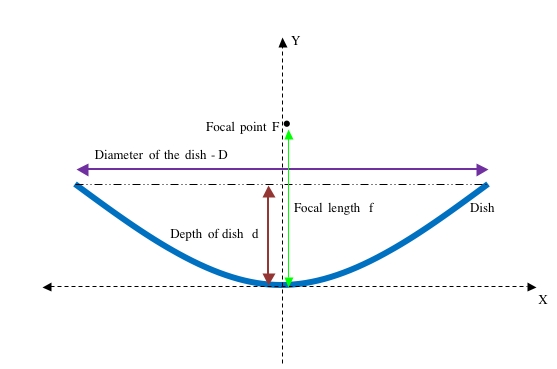
Finding the focal length of a parabolic dish
<math> f = \frac {D^2}{16d} </math> where D is the diameter of the dish and d is the depth of the dish