Diodes: Difference between revisions
(added circuit symbol) |
(added some info and pic) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==What are the electrical characteristics of a diode?== | ==What are the electrical characteristics of a diode?== | ||
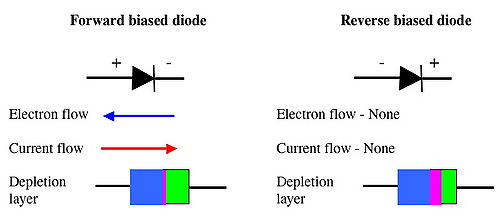
A diode is analogous to a valve that only allows electrons to flow in one direction. When the anode is more positive than the cathode, the diode is said to be'''forward bised''', and electrons can flow from cathode to anode. (conventional current is said to flow in the opposite direction). In this orientation the depletion layer becomes very thin (the valve opens) | |||
When the cathode is more positive than the anode, the depletion layer becomes much wider, preventing the flow of electrons and hence stopping current flow. | |||
[[Image:Vk4yeh_diode-2.jpg | 500px]] | |||
Revision as of 12:12, 11 October 2008
What is a diode?
In its simplest state, a diode is an electrical device that allows current to flow in one direction but not the other.
What is the circuit symbol for a diode?
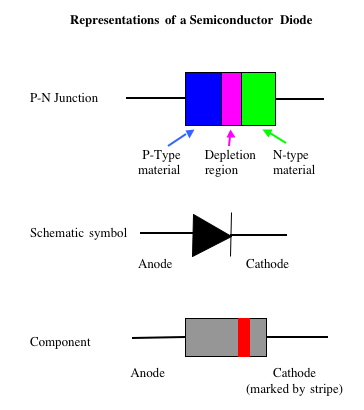
What is a diode made of?
Semiconductor diodes are constructed of layer of N-Type semiconducting material joined to a layer of P-Type semicondictor material. Beteen these is a depletion layer that varies in thickness depending of the voltage bias across the diode.
How does the structure of a diode relate to its circuit symbol?
What are the electrical characteristics of a diode?
A diode is analogous to a valve that only allows electrons to flow in one direction. When the anode is more positive than the cathode, the diode is said to beforward bised, and electrons can flow from cathode to anode. (conventional current is said to flow in the opposite direction). In this orientation the depletion layer becomes very thin (the valve opens)
When the cathode is more positive than the anode, the depletion layer becomes much wider, preventing the flow of electrons and hence stopping current flow.