Log Periodic (LPDA): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(more info and math to follow) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[Image:Vk4yeh_lpda_basic.jpg |300px]] | [[Image:Vk4yeh_lpda_basic.jpg |300px]] | ||
As can be seen in the diagram, one unusual feature of an LPDA is the "crossing over'' of the feed lines for each successive dipole in the array - giving a relative phase shift at each dipole of <math>180^0 ,/math>. | As can be seen in the diagram, one unusual feature of an LPDA is the "crossing over'' of the feed lines for each successive dipole in the array - giving a relative phase shift at each dipole of <math>180^0 ,</math>. | ||
The LPDA is capable of providing maximum:minimum frequency ratio of nearly 2:1 when appropriate design parameters are used. | The LPDA is capable of providing maximum:minimum frequency ratio of nearly 2:1 when appropriate design parameters are used. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Why is it called Log periodic?== | ==Why is it called Log periodic?== | ||
In this antenna the electrical properties vary loagithmically with the frequency. For a simple three frequency antenna for example ( see the diagram below), the resonant frequencies can be named: | |||
f1, f2, and f3 | |||
The dipole lengths (see the diagram below) can be named l1, l2 and l3 | |||
[[Image:Vk4yeh_lpda-2.jpg | 300px]] | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
* [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log-periodic_antenna Wikipedia article] | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Log-periodic_antenna Wikipedia article] | ||
Revision as of 01:12, 20 August 2008
Log Periodic Dipole Array - (LPDA)
What is it?
The log periodic Dipole Array (LDPA) is a multi-frequency antenna compose of a series of driven elements parallel to each other. One of the advantages of the LDPA is that each on each frequency that it is designed for the following essential characteristics of an effective antenna remain almost constant:-
How does it work?
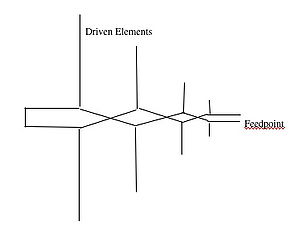
The basic shape of an LPDA is shown in the diagram below. All the elements are driven as all are connected to the feedpoint. The construction is of a series of dipoles of different lengths and different spacings. At a particular frequency, one of the elements will be resonant and the others will not.
As can be seen in the diagram, one unusual feature of an LPDA is the "crossing over of the feed lines for each successive dipole in the array - giving a relative phase shift at each dipole of <math>180^0 ,</math>.
The LPDA is capable of providing maximum:minimum frequency ratio of nearly 2:1 when appropriate design parameters are used.
Typically, Gain is in the region of 7.4dBd
Why is it called Log periodic?
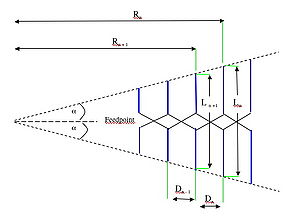
In this antenna the electrical properties vary loagithmically with the frequency. For a simple three frequency antenna for example ( see the diagram below), the resonant frequencies can be named:
f1, f2, and f3
The dipole lengths (see the diagram below) can be named l1, l2 and l3