Rectifier Circuits: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
[[Image:Fullwave.rectifier_1.png | 700px]] | [[Image:Fullwave.rectifier_1.png | 700px]] | ||
{{electronics}} | |||
Latest revision as of 17:25, 8 April 2009
related wiki pages : Electronic Theory, capacitors. Inductors, Voltage, Current, Oscillator Design, Power Supply Design. Filters
What is a Rectifier
A rectifier converts Alternating Current (AC) to Direct Current (DC). This is usually achieved by using a diode, which allows current to flow only in one direction.
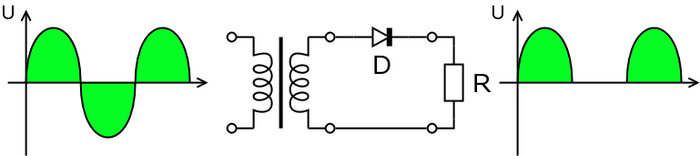
Half-wave Rectifier
copied from Wikipedia under the licensing agreement of the author.
The circuit above illustrates the effect of a single diode in an AC line. The effect is that half of the AC sine curve is "chopped off". This is a very inefficient way of rectifying AC, but may be used to reduce power to a resistive load R.
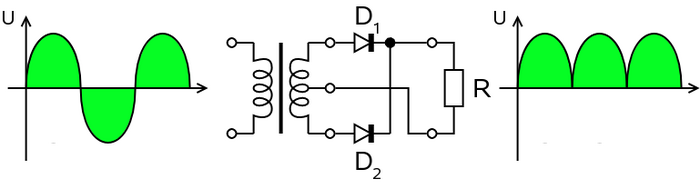
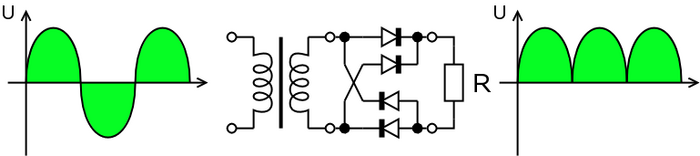
Full-wave Rectifier
Two diode - centre tapped transformer
Four diode or bridge rectifier
| Electronic Theory | |
| Physical quantities | Current * Gain * Impedance * Power * Q of a circuit * Radiated Power Measurement * Reactance* Resistivity * Resonance * Voltage |
| Components | Baluns * Bipolar-Junction Transistors * Capacitors * Diodes * Inductors* Lasers * Microphones * Resistors * Transformers * Wire |
| Circuits | Attenuators * Digital Signal Processing (DSP) * Dummy load * Filters * LC filters * Power Supply Design * Rectifier Circuits |
| Design | Amplifier Design * Oscillator Design |
| Electromagnetic Waves | Relative power (Decibels) * Harmonics * Interference and BPL |