Electromagnetic wave: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(added some detail probably needs more) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
* Period = 1/frequency <math> p = \frac {1}{f} </math> | * Period = 1/frequency <math> p = \frac {1}{f} </math> | ||
{{electronics}} | |||
{{propagation}} | |||
Revision as of 17:26, 8 April 2009
Related wiki pages: SWR, Propagation, Electronic Theory, harmonics
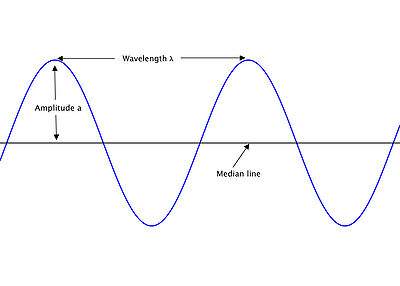
The image below is of a pure sine wave <math> y = sinx </math>
- The Amplitude of the wave a is the distance from the median line of the wave to either a peak or a trough.
- The wavelength <math> \lambda </math> is the distance betwwen two corresponding point on successive waves, and is measured in metres.
- The period of a wave is the time it takes for it to pass a fixed reference point, and is measured in seconds.
- Frequency is the number of waves that pass a fixed reference point per second, with units Hertz (Hz) where 1 Hz = 1 complete cycle per second.
The velocity of electromagnetic waves is close to the speed of light in the atmosphere, approximately 300 000 000 m/s.
Some Math
- Velocity = Frequency x Wavelength <math> v = f \times \lambda </math>
- Period = 1/frequency <math> p = \frac {1}{f} </math>
| Electronic Theory | |
| Physical quantities | Current * Gain * Impedance * Power * Q of a circuit * Radiated Power Measurement * Reactance* Resistivity * Resonance * Voltage |
| Components | Baluns * Bipolar-Junction Transistors * Capacitors * Diodes * Inductors* Lasers * Microphones * Resistors * Transformers * Wire |
| Circuits | Attenuators * Digital Signal Processing (DSP) * Dummy load * Filters * LC filters * Power Supply Design * Rectifier Circuits |
| Design | Amplifier Design * Oscillator Design |
| Electromagnetic Waves | Relative power (Decibels) * Harmonics * Interference and BPL |
| Propagation and radio wave theory | |
| Propagation | Aurora * E-Skip * IPS * Lightning scatter * Meteor scatter * Satellites * Trans-Equatorial Propagation * Tropospheric ducting |
| Interference | QRM * QRN |
| Theory | Electromagnetic Waves * Frequency Wavelength and Period |